Infraredlight,commonlyreferredtoas“IR”,isacom-
mon,easy-to-use,lowpowerandlow-costmediato
transmitinformation.Amongthefew“wireless”commu-
nicationchoices,IRhasthesignificantadvantageof
compatibilitywithhundredsofmillionsofelectronic
deviceswithIRports(i.e.,laptopPCs,PDAs).
ThevastmajorityofIR-capabledevicesarecompatible
withasetofstandardsestablishedbytheInfraredData
Association,orIrDA
®
.Thesestandardsincludeguide-
linesforimplementingtheIRPhysicalLayer(IrDA
SerialInfraredPhysicalLayerspecification),ensuring
thatIRcommunicationcanbeestablishedthroughfree
spacebetweentwodissimilardevices.
Thisdocumentdescribesthefundamentalsofthe
infraredphysicallayer,theIrDAstandardandselecting
theproperdiscreteemitterandphotodiode
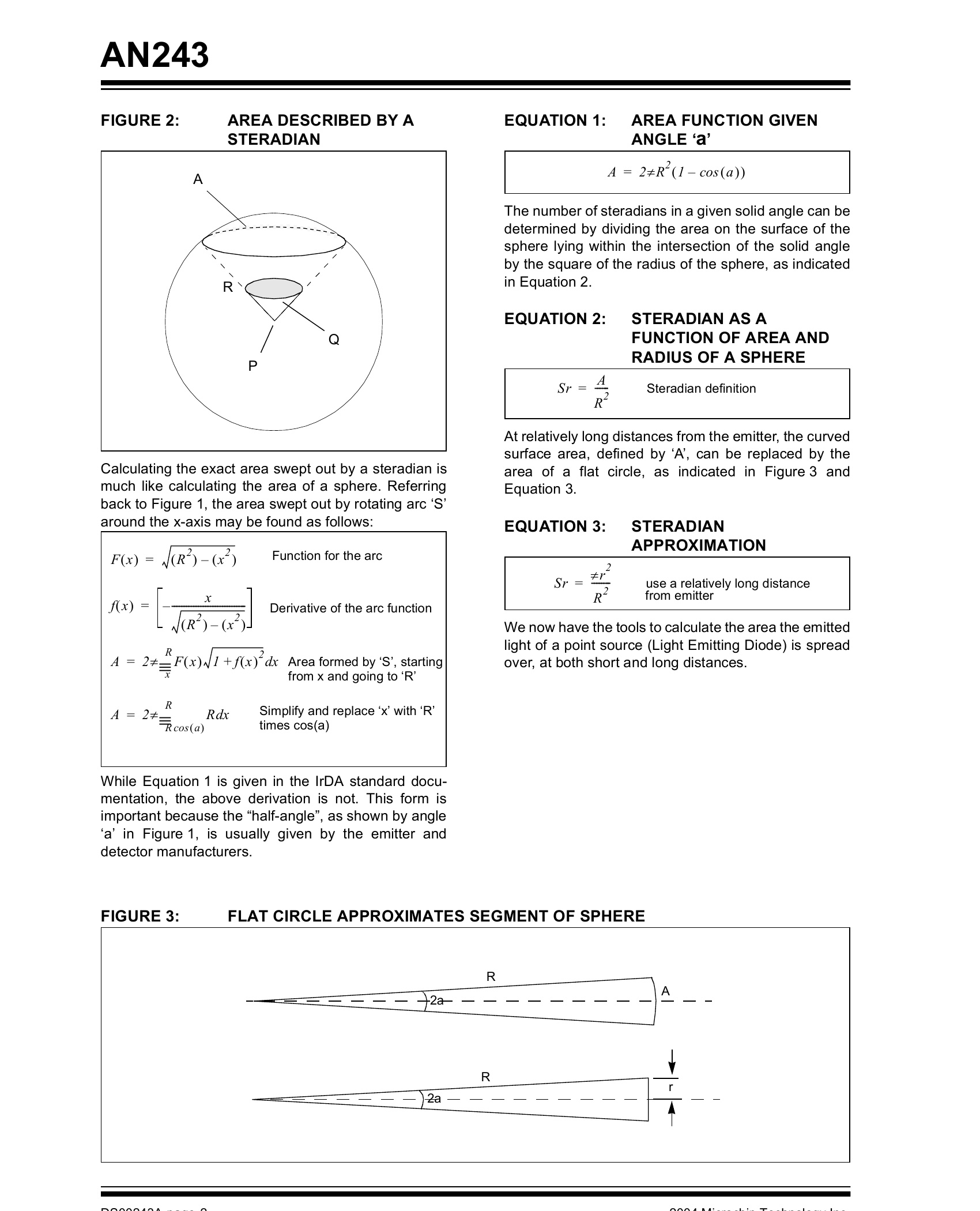
componentsforcircuitimplementation.MAN243FundamentalsoftheInfraredPhysicalLayerTounderstandthesteradian,wewillfirstconsidertheAuthor:PaulBarnaradian.Theradianisdefinedastheangle‘a’thatMicrochipTechnologyInc.SteveSchlangerproducesanarc‘S’thatisequalinlengthtotheradius‘R’andisequalto360/2πdegrees(~57°17’46.6”).AegisTechnologiesLLCThearciscreatedby

暂无评论